The ‘T’ Type 1959 - 1972
By 1959 it had become urgent to replace the dated ‘W’ Type which had a GRW (Gross Vehicle Weight) of 8 tons 11 cwt when new regulations permitted 14 tons GRW of four wheels.
Chief Engineer C.K. Edwards had retired, and an abortive attempt at a replacement ended in failure under the guidance of his successor.
Tom Tillson was recruited from rivals Dennis Bros. and design of the ‘T’ type was pursued with urgency.
1959 the ‘T’ type
The T type introduced in 1959 has the distinctive fibreglass front which was fitted to the wooden framed coach built cab. Only the TW and TY cabs featured the distictive grilles above the headlights and it is thought that with the introduction of the TY Revopak the grilles were no longer a feature. Along with the new ‘TY’ chassis came the Pakamatic aluminium alloy framed compression body. The Pakamatic can be recognised by the hopper side arms that extend along the body to produce the lifting motion to raise the hopper clear when the body is tipped.

1960 The TW Fore & Aft tipper
As a stop gap measure the TW was introduced with the ‘W’ type chassis but the new ‘T’ type cab and a redesigned Fore & Aft tipping body, the vast majority with Power Press compression. Distinctive features on the cab are the grilles above the headlights and the flat roof compared to the later ‘T’ series cabs.

1962? The TN Pakamatic
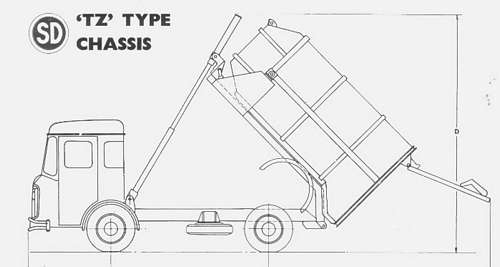
A narrow version of the ‘T’ series was introduced, designated TN, for use in areas with narrow lanes or alleyways. The overall width was 6 ft 6 ins compared to the standard 7 ft 5 1/4 ins. The TZ chassis appeared in 1964 and around this time the TX was also introduced.

1969 The Paka Ejector
Unlike the Pakamatic’s tipping method the load was discharged by a pusher plate and the hopper raised out of the way by hydraulic rams to solve the problem of the instability created by tipping the loaded body. This was the ejection method adopted for the later Revopak. I have been unable to find any photos of a Paka Ejector beyond the one shown as caption 141 in Kaleidoscope of S&D
Mid 1960’s Modifications to the Fore & Aft tipper
The tipping method was altered to utilise separate hydraulic rams for forward and backward tipping of the body in place of the twin rams that performed both operations. The hydraulic cylinders for the Power Press were mounted inside the body instead of externally.
1971 The Revopak
As a replacement for the Pakamatic, the Revopak has rotating tines in the hopper to crush and compress the refuse. The refuse is discharged by a pusher plate as mentioned above.

Chassis Type Definitions
TW 8 tons 11 cwt GVW (As ‘W’ Type) 8’ 6” wheelbase 6’ 10 “ or 7’ 5 1/4” wide, 10’ 9” and 11’ 6” wheelbase 7’ 5 1/4” wide, 13’ 0” wheelbase 8’ 0” wide.
TN 8.75 tons GVW (N=narrow) 8’ 0” or 9’ 5” wheelbase 6’ 6” wide
TZ 12.50 tons GVW 11' 9" wheelbase 7' 0" wide
TX 13.75 tons GVW 12' 10" wheelbase 7' 6" wide
TY 15/16 tons GVW 13'- 0"/ or 15'- 0" wheelbase 8' 0" wide
Almost 11,000 T series vehicles were produced [Kaleidoscope caption 128] including 1020 TW’s [Kaleidoscope caption 132] 160 TX’s and 4,400 TY’s [Kaleidoscope caption 130]